Table of Contents
Marine Engineers Q and a series part 4
Welcome to the fourth installment of our Marine Engineer Q&A series! In this blog, we’ll be answering some of the most frequently asked questions about the exciting and challenging field of marine engineering.
Marine engineering is a highly specialized field that involves the design, construction, and maintenance of ships and other ocean-going vessels. It is a dynamic and constantly evolving industry that requires a blend of technical expertise and problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned marine engineer or just considering a career in this field, this blog will provide valuable insight into what it takes to be a successful marine engineer.
So, let’s dive into some of the most commonly asked questions and get started!
Read the related post:- Marine 4th Engineer Interview Questions: 20 Best for Marine Exams
Q 1- How Slippage Occurs in Fully Assembled or Semi-Assembled Crankshafts During Shrink Fit Identified?
Ans- In a fully-built or semi-built type crankshaft, the witness mark is a reference point to identify any slippage that might occur during the shrink-fit process. A witness mark is a minor groove or line created on the surface of the crankshaft before it is subjected to the shrink-fit process. The witness mark serves as a visual reference point to determine if any movement or slippage occurred during the crankshaft installation in the engine block.
If the crankshaft has moved or slipped during the shrink-fit process, the witness mark will no longer align with the corresponding reference mark on the engine block. The witness mark can indicate that the crankshaft is not adequately secured in the engine and may cause issues with the engine’s performance and reliability.
Therefore, it is important to carefully inspect the witness marks after the shrink-fit process to ensure that the crankshaft has been properly installed and secured. Inspection of the witness mark is a critical step in ensuring the proper function and longevity of the engine.
Q 2- Why is the start of injection delayed on a jerk type fuel pump with VIT?
Ans- Raising the barrel can delay the beginning of injection in a VIT (Variable Injection Timing) equipped jerk-type fuel pump. The VIT system is used to adjust fuel injection timing in internal combustion engines. It allows the fuel injection timing to be advanced or retarded depending on the operating conditions of the engine.
Q 3- What harm does it do when a diesel engine generator over speeds?
Ans- The over-speeding of a diesel engine driving an electric generator can cause damage to the windings and result in reduced performance and efficiency. Over-speeding occurs when the engine exceeds its maximum operating speed, which can be caused by various factors, such as a failure in the speed governor, an increase in load on the generator, or a malfunction in the engine’s fuel system.
An engine over-speed can strain the generator and its components, including the windings. Over time, this can cause the windings to break down, leading to insulation failures and short circuits. Winding damage can result in reduced performance, increased heat generation, and increased risk of loss, which can cause significant downtime and repair costs.
It is essential to closely monitor the engine’s and the generator’s operating speed and perform regular maintenance to ensure that the speed governor and other critical components are functioning correctly To prevent over-speeding and the resulting damage to the windings. In addition, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maximum operating speed and to avoid overloading the generator.
Q 4- In a large, slow-speed main Engine, which parts are under tension when the engine is running?
Ans-In a large, slow-speed main engine, tie rods are typically under tension when the engine is running. Tie rods are components of the engine’s assembly, which connect the cylinder block and engine bed plate.
The up-and-down motion of the pistons generates tension in the tie rods as the engine runs. This creates a force that tries to pull the connecting rod away from the crankshaft, which counteracts the tension in the tie rods.
Maintaining proper tension in the tie rods is essential, as this helps to ensure the stability and reliability of the engine’s assembly. Insufficient tension can cause the engine assembly to loosen or become misaligned, resulting in increased wear and tear on the engine components and reduced performance and efficiency.
To ensure that the tie rods are correctly tensioned, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and inspection is essential. This typically involves regular tightening and checking the tie rods to ensure they are in good condition and functioning correctly.
Q5– How to Identify Metals in the Engine Room?
Answer: By using visual inspection and conducting a spark test.
Q6: How would you define the terms ‘Flash Point’ and ‘Fire Point’?
Answer: The Flash Point refers to the minimum temperature at which a substance can produce vapor to form an explosive mixture with air. On the other hand, the Fire Point is the temperature at which the vapors of a substance can sustain combustion for at least 5 seconds when exposed to an open flame.
Q7: How would you define the term ‘creep’ about materials?
Answer: Creep typically pertains to metals and describes the gradual plastic deformation of a material when subjected to constant stress over time.
Q8: How do you define ‘Fatigue’ in materials?
Answer: Fatigue refers to the weakening or failure of a material resulting from continuous or repeated stress applications.
Q9: How would you describe the fire triangle and the approach to address each component?
Answer: The fire triangle represents the three elements necessary for a fire: fuel, oxygen (air), and heat (combustible material). Each triangle component must be disrupted or removed to combat a fire.
Q10: How would you describe a ‘bursting disc’ in engine mechanics and its function?
Answer: A bursting disc acts as a safety mechanism in an engine designed to safeguard against the detrimental consequences of crankcase explosions. While similar in function to a safety valve, it’s notably larger. In an internal engine pressure surge due to an explosion, the disc is designed to rupture, thus releasing the excessive pressure to prevent further damage.
Q11: Can you explain the concept of a ‘shaker piston’?
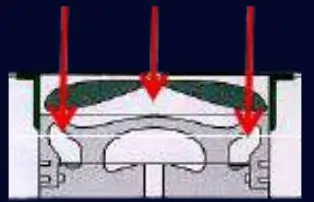


Answer: A shaker piston is named after the distinct “shaker space” found within its piston crown. As related diagrams illustrate, this space often consists of two compartments interconnected by channels or bores. In modern engines, where the piston can move up and down between 7 to 17 times a second, the oil within this space undergoes vigorous agitation, akin to the action in a shaker. This continuous movement facilitates the crucial cooling of the combustion chamber’s base.
Q12: Is using the crank web deflection values from the testbed record as a comparative measure for on-board conditions appropriate?
Answer: No. The testbed record values verify that the engine alignment met the specified tolerances at that time.
Q13: What standard method is employed to lubricate bearings in compact high-speed diesel engines?
Answer: The preferred lubrication method in compact, high-speed diesel engines is “pressure lubrication.” This method uses a pump to deliver oil under pressure directly to the engine’s bearings and other critical components. The pressurized oil provides a protective film between the bearing surfaces to reduce friction and wear and helps remove heat from the bearing surfaces, ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. This system is especially crucial in high-speed engines where components move rapidly and are more prone to wear and tear.
Q14: Why is an inlet grid positioned within the exhaust gas casing, along the gas flow trajectory, before its entrance into the turbocharger?
Answer: The inlet grid inside the exhaust gas casing serves a vital function in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of the turbocharger. As exhaust gases flow from the engine towards the turbocharger, residual unburned carbon particles might be present. These particles can damage the turbocharger’s delicate components over time. The inlet grid acts as a filtration system, capturing and filtering these unburned carbon particles. This prevents potential wear and damage to the turbocharger and ensures that only clean and efficient exhaust gases are used to drive it, optimizing its performance and durability.
Q15: What is tie rods’ primary role in designing large, low-speed diesel engines?
Answer: They are designed to handle most tensile stresses from the firing forces experienced during engine operation.
Q16: What factor primarily determines the minimum clearance for thrust bearings?
Answer: The necessity to enable the thrust pads to pivot, forming an oil wedge for lubrication and effective operation.
Q17: What factors might lead to the cracking of a piston crown?
Answer: Factors include accumulations in the cooling chambers, mistimed fuel injection causing direct fuel impingement, and inadequate flow of piston cooling oil.
Q18: What information is conveyed by the NLGI number assigned to grease?
Answer: It denotes the grease’s consistency, indicating its level of fluidity or solidity.
Q19: Which layer primarily provides fatigue strength in a thin shell bearing?
Answer: The “overlay” layer of the thin shell bearing is crucial for its fatigue strength. This specific layer is engineered to withstand the repetitive stresses and strains experienced during the bearing’s operation, thus allowing the bearing to resist fatigue and potential failure over prolonged use. The overlay ensures the bearing’s durability, especially under varying load conditions.
Q20: Among the various bearing types, which is predominantly chosen for the main and connecting rod bearings in contemporary diesel engines?
Answer: The “Precision insert” bearing is most commonly selected. This bearing type is favored because of its precise design and ability to be replaced easily. In modern diesel engines, which demand high reliability and performance, the precision insert bearings offer an optimal blend of durability and ease of maintenance, making them the preferred choice for main and connecting rod applications.
Q21: How do diesel engine driving alternators maintain a consistent speed without significant variations?
Answer: This consistent operation is achieved by incorporating “load sensing devices.” These devices detect changes in the engine’s load and promptly adjust its speed, ensuring it remains stable and avoids significant fluctuations. This improves the engine’s efficiency and provides the smooth operation of the alternator it drives.
Q22: What is the consequence of having an overly large tappet clearance between the rocker arm tappet and the exhaust valve stem?
Answer: If excessive tappet clearance between the rocker arm tappet and the exhaust valve stem, the valve’s operation is impacted. Specifically, the valve will initiate its opening process later and complete its closing process earlier than intended. This altered timing can affect engine performance and efficiency, as the valve won’t be synchronized with the engine’s combustion cycle, potentially leading to incomplete combustion and other related issues.
Q23: What factors can contribute to a main engine’s diminished power output?
Answer: Factors such as elevated scavenge air temperatures, obstruction in the turbocharger’s air suction filter, and blow-by occurring in one or multiple units can all reduce the power generated by the main engine. These conditions can hinder optimal combustion and engine efficiency, affecting the engine’s performance.
Q24: Which instrument is commonly employed to measure the clearances of main bearings?
Answer: The “Telescopic feeler gauge” is typically used for this purpose.
Q25: Why is a duplex filter unit’s preferred configuration for a continuously operating diesel engine?
Answer: The advantage of a duplex filter unit is that it allows for the replacement of filter elements without causing any disruption to the engine’s ongoing operation.
Q26: In contemporary 4-stroke medium-speed marine diesel engines, what mechanism facilitates the rotation of exhaust valve spindles?
Answer: “Rotocaps” are employed to achieve this function.
Q27: Among various crankshaft designs, which offers a lighter weight for comparable power specifications?
Answer: The “Semi-built, all welded type” crankshaft is notably lighter for similar power needs.
Q28: What causes the drive gear or pinion to disengage from the flywheel after initiating an engine using a Bendix drive unit?
Answer: It’s due to the increased rotational speed of the flywheel.
Q29: While fuels produced in a refinery typically begin as sterile, at what stages might contamination arise?
Answer: Contamination can occur when fuels are stored at the refinery, stored on board a vessel, and during transportation to distribution locations.
Q30: In the case of a fully built or semi-built crankshaft, what method is used to detect any slippage at the shrink fit area
Answer: One can identify slippage by examining the reference witness mark provided.
Blog Post Conclusion
As we wrap up the fourth installment of the Marine Engineers Q&A series, it’s evident that the vast expanse of marine engineering never ceases to inspire curiosity and learning. This series serves as a testament to the intricacies and complexities faced by marine engineers daily. From the minutiae of engine components to the broader aspects of marine fuel and vessel design, each question and answer paints a vivid picture of the challenges and solutions in the maritime realm.
The questions addressed in Part 4, in particular, highlight the depth of knowledge required to maintain and optimize the functionality of marine engines and their associated components. Understanding the specificities of tools, the behavior of different materials under stress, and the intricacies of engine design are paramount to ensuring marine vessels’ safe and efficient operation.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of the marine engineering field is evident in the questions posed.
We hope it has been an enlightening journey for those following this series. The continuous thirst for knowledge and the dedication to precision exemplified by marine engineers are commendable. As we look forward to the next installment, we remain committed to delving deeper into this fascinating domain, bringing forth more insights and clarifications for seasoned professionals and marine enthusiasts alike.
Thank you for joining us in this exploration, and stay tuned for more enlightening discussions in the Marine Engineers Q&A series!
