Table of Contents
Diesel engine crankshaft
In this post on the diesel engine crankshaft, we will discuss the Crankshaft Of Marine Diesel Engines. I have explained everything from the basic design to the crankshaft’s alignment technology. This post will be helpful for marine engineers and students. Diesel engine crankshaft is an internal combustion engine’s most mysterious, complicated, and crucial component.
During the engine running period, Heavy operational loads are experienced by the crankshaft.
The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion into rotary motion developed due to the combustion of fuel and air inside the combustion chamber. This rotary motion is further transmitted for various applications. In the case of Propulsion engines, it is used for rotating the Propeller, and for Generators, it is used for turning the Alternator,
Other components’ function depends upon the correct revolution of the Crankshaft, such as the Camshaft for the firing order and fuel timing. The Engine will stand a standstill if a single part of the Crankshaft fails.
Due to the operation’s nature, the Diesel engine crankshaft is subjected to several forces like bending and twisting action upon the Crankshafts depending upon the applications’ nature. These forces are due to various factors not limited to the piston’s weight, combustion loads, axial load from propellers, compression loads of webs on journals, and generators’ heavy torque loads.
The Anatomy of a Diesel Engine Crankshaft
Main Journals: These are like the crankshaft’s anchors. They fit into main bearings and act as the central axis that the crankshaft spins around.
Connecting Rods: These arms connect to the crankshaft’s special parts called crank pins. They help transfer power from the engine’s pistons to the crankshaft.
Crank Webs: Think of these as bridges. They connect the crank pins (the special parts on the crankshaft) to the main journals. They help the crankshaft stay strong and sturdy.
Counterweights: These are like weights on a seesaw. They help balance the crankshaft, ensuring it doesn’t wobble or shake too much when the engine runs.
So, in simple terms, the crankshaft has main journals that fit into bearings, connecting rods that link to special parts called crank pins, crank webs that act like bridges, and counterweights that keep everything balanced. All these parts work together to make sure the engine runs smoothly.



The crankshaft in a marine diesel engine may seem like a basic metal rod, but it’s a crucial part of the engine’s operation. Let’s break it down into more understandable words.
Think of the crankshaft as the engine’s “power transformer.” Its main role is to convert the piston’s up-and-down movement into the spinning power that drives the boat forward. To make this happen, it’s designed with some important parts.
First, there are the main and connecting rod journals. Picture them as the connectors between the pistons and the crankshaft. They must be carefully crafted to ensure the energy is smoothly transferred.
Now, consider the counterweights. These act like the balancing weights on a playground seesaw, ensuring everything stays steady. They prevent the engine from vibrating too much and keep it running smoothly.
In simple terms, the crankshaft is like the silent hero of your marine diesel engine. It works quietly and efficiently to keep your boat moving.
So, the next time you’re out on the water, remember that this seemingly ordinary metal rod is doing something extraordinary beneath the surface.
Materials Used in Crankshaft Manufacturing
High-strength steel alloys take the spotlight regarding the materials used in manufacturing crankshafts. Designers carefully select these materials to create crankshafts with the most desirable properties. These steel alloys mostly consist of iron, with tiny amounts of carbon, typically between 0.25 and 0.45 %.
This carbon content is often expressed as “25 to 45 points” of carbon. These steel alloys combine additional alloying components, each carefully selected to provide the finished product with particular qualities.
These desired properties encompass hardness, both on the surface and in the core of the crankshaft, ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, endurance limit fatigue strength, ductility, impact resistance, corrosion resistance, and resistance to high-temperature conditions.
The stuff mixed into these carbon steels to make crankshafts strong and durable includes manganese, chromium, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, cobalt, vanadium, and sometimes aluminum and titanium. Each of these things adds different qualities to the material, making it special.
And here’s an important part: the amount of carbon in the mix is a big deal. It decides how strong and hard the crankshaft can get when heated and treated.
So, in simple terms, it’s like making a recipe with different ingredients. These ingredients are carefully chosen to ensure the crankshaft is tough and performs well. And how much carbon is used is like deciding how well-cooked your dish will be. It’s all about getting the right mix for a strong and reliable crankshaft.
Types of the Diesel engine crankshaft
- Semi Built
- Fully Built
- Welded
Semi-Built Diesel Engine Crankshaft: In this design, crank throws, and pins are cast separately. The same forging is used for throws with two webs and crank pins. Main journals are separately machined and shrink-fitted into the drilled holes of crank webs. The advantage is a single forging for crankpins and webs, reducing weight without compromising strength. However, shrink fitting can cause hoop stresses leading to cracks, preventable through unit balancing.
Fully Built Diesel Engine Crankshaft: All components are fabricated separately and shrink-fitted in this design. Webs, crankpins, and main journals are made separately. Crank pins and journals are machined and shrink-fitted into heated webs with matching holes. Dowels for location are not recommended as they can create stress risers.
Welded Diesel Engine Crankshaft: This type involves welding together various crankshaft parts. The welds must be high-quality to ensure the crankshaft’s integrity and performance. Proper welding techniques and material selection are critical to avoid weaknesses or failures in the crankshaft.
Reasons for Diesel engine crankshaft Failure
Crankshafts in diesel engines are essential components, but they can fail due to various reasons. Here are eight common causes of diesel engine crankshaft failure:
- Over Speeding of Engine on Load: Running the engine at excessively high speeds while under a heavy load can stress the crankshaft tremendously, leading to potential failure.
- Eddy Currents/Stray Currents from a Faulty Alternator: Electrical issues, such as eddy currents or stray currents caused by a malfunctioning alternator, can damage the crankshaft over time.
- Fatigue Failure from Bored Oil Hole Lip: Over time, fatigue can set in, especially around the edges of oil holes in the crankpin. This can weaken the crankshaft and ultimately lead to failure.
- Heavy Vibration and Torsion: Excessive vibrations and torsion in the engine can cause cracks in the crankpin and main journals of the crankshaft, compromising its integrity.
- Lubrication Starvation: Inadequate lubrication is a common culprit behind bearing failures, which can significantly damage the crankshaft.
- Hydraulic Lock Due to Cylinder Over-Pressurization: If water leaks into the cylinders, it can cause a hydraulic lock, resulting in excessive pressure within the cylinder. This pressure can exert excessive force on the crankshaft, potentially causing damage.
- Crack Development on Fillets: Cracks that develop in the fillets (the curved transitions between the journals and webs) can weaken the crankshaft, eventually leading to failure.
- Misaligned Crankshaft: If the crankshaft is not properly aligned, it can experience uneven stress, causing premature wear and eventual failure.
Causes of Diesel Engine Crankshaft Misalignment
- Damaged Main Bearing
- Disturbed Line Bore in Overhung Crankshaft Arrangement
- Disturbed Line Bore in Underslung Crankshaft Arrangement
- Incorrect Foundation Bolt Tightness
- Cracks in Bearing Saddle
- Loose Main Bearing Bolts
- Excessive Piston Forces Lead to Bending
- Crankcase Fire/Explosion
- Cracked Bearing Housing
- Broken Tie Bolts
- Structure Weakening from Erosion and Corrosion
How to prevent Diesel engine crankshaft failure
- Address Vibration Promptly: Immediately eliminate engine vibration and avoid running the engine for extended periods with heavy vibrations.
- Regularly Inspect Foundation Bolts: Check the engine’s foundation bolts regularly to ensure they are secure.
- Maintain Engine Tuning: Keep the engine well-tuned to prevent undue stress on the crankshaft.
- Monitor Crankshaft Deflection: Regularly check and monitor the deflection of the crankshaft to detect any potential issues early.
- Ensure Proper Alignment: Keep the engine and alternator properly aligned within prescribed limits to prevent misalignment-related problems.
- Check for Metal Particles: During maintenance, inspect the lube oil filter disc for any metal particles that could indicate problems.
- Periodic Lube Oil Sampling: Get the lube oil sampled and checked periodically to assess its quality and identify potential issues.
- Governor Maintenance: Periodically maintain the engine’s governor to prevent malfunctioning that could lead to over-speeding.
- Avoid Overloading: Prevent overloading the engine to avoid excessive stress on the crankshaft.
- Watch Engine Speed: Avoid running the engine at excessively high speeds to protect the crankshaft.
- Conduct Instrument Tests: Perform function tests on various engine instruments to ensure they are operating correctly and can help identify potential issues.
Following these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of diesel engine crankshaft failure and prolong the engine’s lifespan.
Primary Symptoms of Diesel Engine Crankshaft Misalignment
- Increased Vibration
- Elevated Body Casting Temperature
- Frequent Loosening or Breaking of Foundation Bolts
- Shims and Dowels Becoming Loose
- Excessive Leakage at Seals
- High Rate of Coupling Failures
- Premature and Frequent Bearing Failures
Measuring and Correcting Diesel Engine Crankshaft Misalignment
When aligning a diesel engine’s crankshaft, there are some basic principles to remember, particularly regarding parallel and angular misalignment. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and steps involved:
1. Reference Points: Maintaining consistent reference points throughout the alignment process is crucial. Any changes to these reference points can result in imperfect alignment.
Components in the Alignment Process:
a. Movable Component: This refers to the part that moves during alignment. In most cases, it’s the generator since it’s easier to adjust than the engine itself.
b. Fixed Component: The prime mover, typically the engine, remains stationary and serves as the reference point for alignment.
Measuring Runout:
a. Shaft Runout: To check for shaft runout, place a dial gauge on a fixed surface and position the pointer at the face of the wheel. Rotate the shaft through a complete revolution, and any changes in the gauge reading indicate an issue with the starting point.
b. Face Runout: This involves placing the dial gauge on a fixed surface and positioning the pointer at the periphery of the flywheel. Rotate the flywheel through a full revolution to measure any off-center diameter readings.
Measuring Parallelism:
To measure the parallelism between two components, turn the shaft by one complete revolution while keeping the dial gauge on a fixed surface and the pointer at the wheel.
Following these steps and principles, you can effectively measure and correct misalignment in a diesel engine’s crankshaft, ensuring proper alignment and optimal engine performance.
Crankshaft Deflection: Understanding the Significance
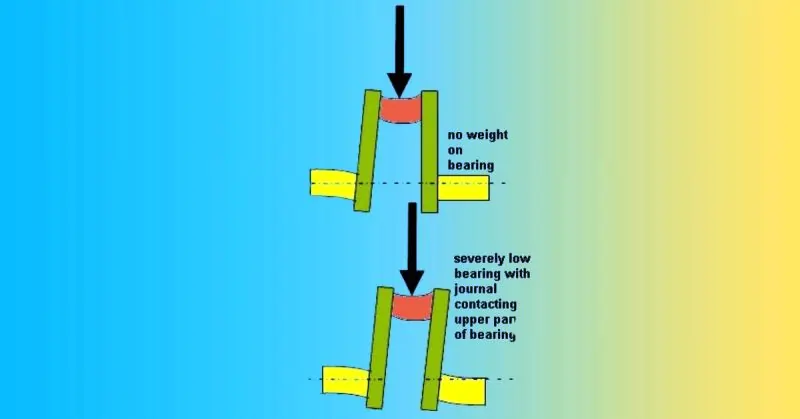


The crankshaft in an engine is a critical component that relies on main bearings for support. These bearings bear the weight of the crankshaft as it rotates. Over time, as the engine runs continuously, wear and tear occur in these bearings. Bearings wearing pattern will depend upon the engine’s various operating conditions.
It is crucial to note that with the wear of bearings, the center axis of the crankshaft will shift in an upward or downward position. Even this slight shift can lead to the crankshaft experiencing stress in its crank webs as it operates. To detect and rectify this problem, it is necessary to measure the crankshaft deflection at the specified intervals per the OEM recommendations.
Here are some key points to keep in mind when measuring crankshaft web deflection:
Consistency in Measuring Conditions: Maintaining consistent measuring conditions is essential to ensure accurate and reliable deflection readings. Any variations in conditions can affect the results.
Measure When the Engine is Cold: To get accurate readings, measure the deflection when the engine is cold. Additionally, it’s advisable for the dial gauge used for measurement to be at a similar temperature as the engine.
For the engine to last as long as possible and to avoid severe fatigue levels that could result in crankshaft failure, it is essential to comprehend and monitor crankshaft deflection.
Crankshaft Deflection Checking Procedure
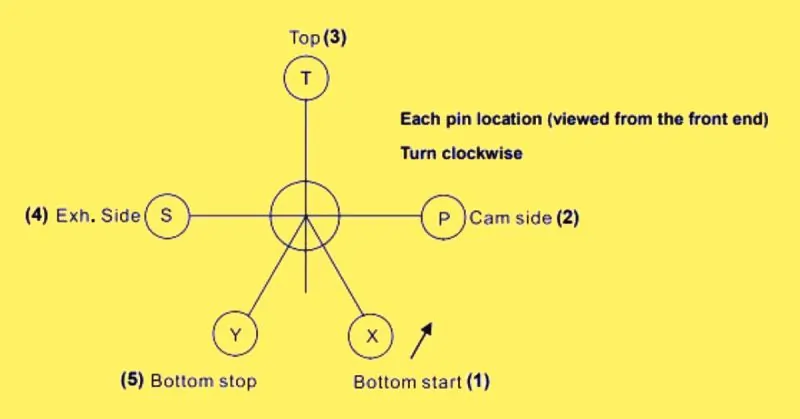


To ensure the proper functioning of an engine, it’s crucial to check the deflection of the crankshaft. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform this procedure:
- Rotate the crankshaft to position 1, the measuring position.
- Set the dial gauge to zero.
- Rotate the crankshaft and take readings at positions 2 to 5. Record only the deviation from the zero setting of the dial gauge.
- Evaluate these recorded readings.
- Note that the reading at position 5 should be nearly the same as at position 1. If there is a significant difference, repeat steps 2 to 5.
The calculations for vertical and horizontal deflections are as follows:
- Vertical deflection (dv) = T – (x + y) / 2
- Horizontal deflection (dh) = P – S
Instructions:
- If the vertical and horizontal deflections exceed the limits specified by the equipment manufacturer, it’s essential to realign the engine and driven machinery.
- Before proceeding with realignment, inspect the bearing metal for any abnormal wear.
- Recheck the deflection by repeating steps 1 to 5.
- Record all measurements accurately for future reference and maintenance purposes.
By following this procedure and adhering to the manufacturer’s limits, you can ensure that the crankshaft operates within the necessary parameters, contributing to the engine’s reliability and longevity.
Benefits of Diesel Engine Crankshaft Alignment
Proper alignment of the diesel engine’s crankshaft offers a range of advantages:
- Enhanced Reliability and Extended Operating Life: When the crankshaft is correctly aligned, it significantly improves the reliability and longevity of the entire machine.
- Reductions in Several Key Areas:
- Spare Parts Consumption: Proper alignment reduces the wear and tear on components, resulting in less frequent replacement of spare parts.
- Maintenance Labor Cost: With reduced wear and tear, maintenance requirements are less frequent and less labor-intensive, resulting in cost savings.
- Production Loss: Improved alignment minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns and downtime, ensuring continuous production processes.
- Need for Standby Arrangements: Reduced downtime means less need for costly standby equipment or contingency plans.
- Enhanced Safety: Proper alignment contributes to safer operating conditions, reducing the risk of accidents or equipment failures.
- Cost of Power Consumption: Improved alignment can lead to more efficient engine operation, lowering overall power consumption and operational costs.
FAQ on “Diesel engine crankshaft”
Q: What is a diesel engine crankshaft?
A: The crankshaft is a key component that converts piston motion into rotational power.
Q: Why is crankshaft alignment important?
A: Proper alignment ensures engine reliability and reduces wear.
Q: What causes crankshaft failure?
A: Factors like misalignment, excessive vibration, and poor maintenance can lead to crankshaft failure.
Q: How can you measure crankshaft deflection?
A: Crankshaft deflection can be measured using dial gauges and specific procedures during maintenance checks.
Conclusion: The Heart of Diesel Power
The diesel engine crankshaft is undoubtedly the heart of diesel power. Diesel Engine performance and life will depend upon the design, construction, and maintenance. You will better appreciate the engineering marvel of the diesel engine crankshaft if you comprehend the ideas covered in this article. The crankshaft, the most mysterious and complicated part of an ICE engine, must be well maintained. The OEM recommendations are to be strictly followed to prevent the crankshaft failure. It would be right to mention that the cost of a crankshaft is 1/3 of the total cost of an Engine.
